Getting started¶
Part 1: Run rosbridge and roboySimulation¶
Before the simulation is run, model paths and IP addresses need to be sourced / specified and ROS messages defined. The following commands can be applied in any terminal, even if some might not be necessary, they don’t do any harm and may save you from hardship later, thus executing all commands is advisable. IMPORTANT: Adapt paths to lead to /roboy-ros-control/ folder!
export GAZEBO_MODEL_PATH=/path/to/roboy-ros-control/src/roboy_models:$GAZEBO_MODEL_PATH
export GAZEBO_PLUGIN_PATH=/path/to/roboy-ros-control/devel/lib:$GAZEBO_PLUGIN_PATH
export GAZEBO_RESOURCE_PATH=/path/to/roboy-ros-control/src/roboy_models:$GAZEBO_RESOURCE_PATH
source /path/to/roboy-ros-control/devel/setup.bash
source /usr/share/gazebo-7/setup.sh
On the Linux/Ubuntu machine, the simulation and ROS server are run. There are two ways to start a simulation: launch files automatically take care of starting a ROS server, gazebo and other plugins and immediately start the simulation. Another option is to start ROS manually using the roslaunch command below. The simulation is run with rosrun. In case you need to change the port on which you want to operate (e.g. because it is already in use), adapt the value of the following command or in the respective launch and make sure to also change the value in the Unity scene.
#option 1:
roslaunch roboy_simulation roboy_moveable.launch
#option 2:
source path-to-roboy-ros-control/devel.setup.bash
roslaunch rosbridge_server rosbridge_websocket.launch port:=9090
rosrun roboy_simulation VRRoboy
NOTE: When running a simulation like VRRoboy / VRRoboy2, plugins which are defined in models WILL NOT be loaded - even though they are supposed to (at least expected from our side), therefore roboy_moveable was implemented in a launch file but is designed to do the same as VRRoboy2.
Part 2: Open the project in Unity¶
One main scene is designed to incorporate all project aspects, including a UI, the simulated Roboy model and more. on the Windows machine, start Unity and open this scene. The only exception poses the PaBi model, which is described in an extra chapter. Open the main scene in all other cases.
Part 3: Setup the scene¶
To receive and display the pose which is simulated on he Linux machine, both machines need to be situated in the same network and the ROS server’s IP address and port needs to be registered in Unity. The following command shows which IP the ROS server is using.
echo $ROS_IP
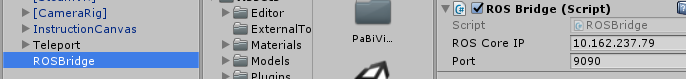
You can reset the simulation with the R key or with both grip buttons on the Vive controller of the GUI Hand. You can also change the key in RoboyManager. Notice: This is not working for all simulations.
Part 4: Using RViz [Optional]¶
RViz is a tool to visualize the simulated Roboy. As soon as values are provided to RViz via ROS, it can display these. Additionally, it visualizes forces, as can be seen when visualising the roboy_moveable.launch simulation in this program.
To start Rviz, open a terminal and type rviz, hit enter after the ROS server started, otherwise it won’t connect to the server. Set Fixed Frame to World (Displays->Fixed Frame) . Add a marker (Add(Button)->marker).